Google Analytics 4: Here’s Everything You Must Know

By July 2023, Google is moving all analytics setup to GA 4 or Google Analytics 4. It wants companies to run on this platform latest by July 2022, so that they have complete one-year data when the complete switchover begins in 2023.
However, there’s a lot to learn for marketers and there’s certainly some confusion or doubts revolving around GA 4. This blog contains information regarding GA 4, how it’s different, and the necessary measures to perform while setting up GA 4.
What Is The Difference Between Universal Analytics And Google Analytics 4?
Introduced in the fall of 2012, Google Universal Analytics is the analytics most people are accustomed to. It contains the regular bounce rate, page views, and all the other familiar metrics.

However, GA 4 with new advancements, aims at understanding website visitors. It’s the new update of Google Analytics. With much precise information available for marketers, the new update has made Analytics robust.
Currently, GA 4 has no API and it includes new metrics such as engagements, screens, and views. So, the new advanced version of Analytics is GA 4, whereas, the former one is Universal Analytics.
What To Do Immediately With Your Google Analytics?

Businesses should switch over to Google Analytics as quickly as they can. Then, there are 2 deadlines to keep in mind. As far as the precise dates are concerned, July 1, 2023, is when the accessible version of universal processing will be disapproved.
For the 360 or paid customers, October 1, 2023, is when their versions will be deprecated.
How To Set Up Google Analytics 4?
These are the steps that you can take for configuring Google Analytics 4 (GA 4):
Step – 1. Access your Google Analytics account.
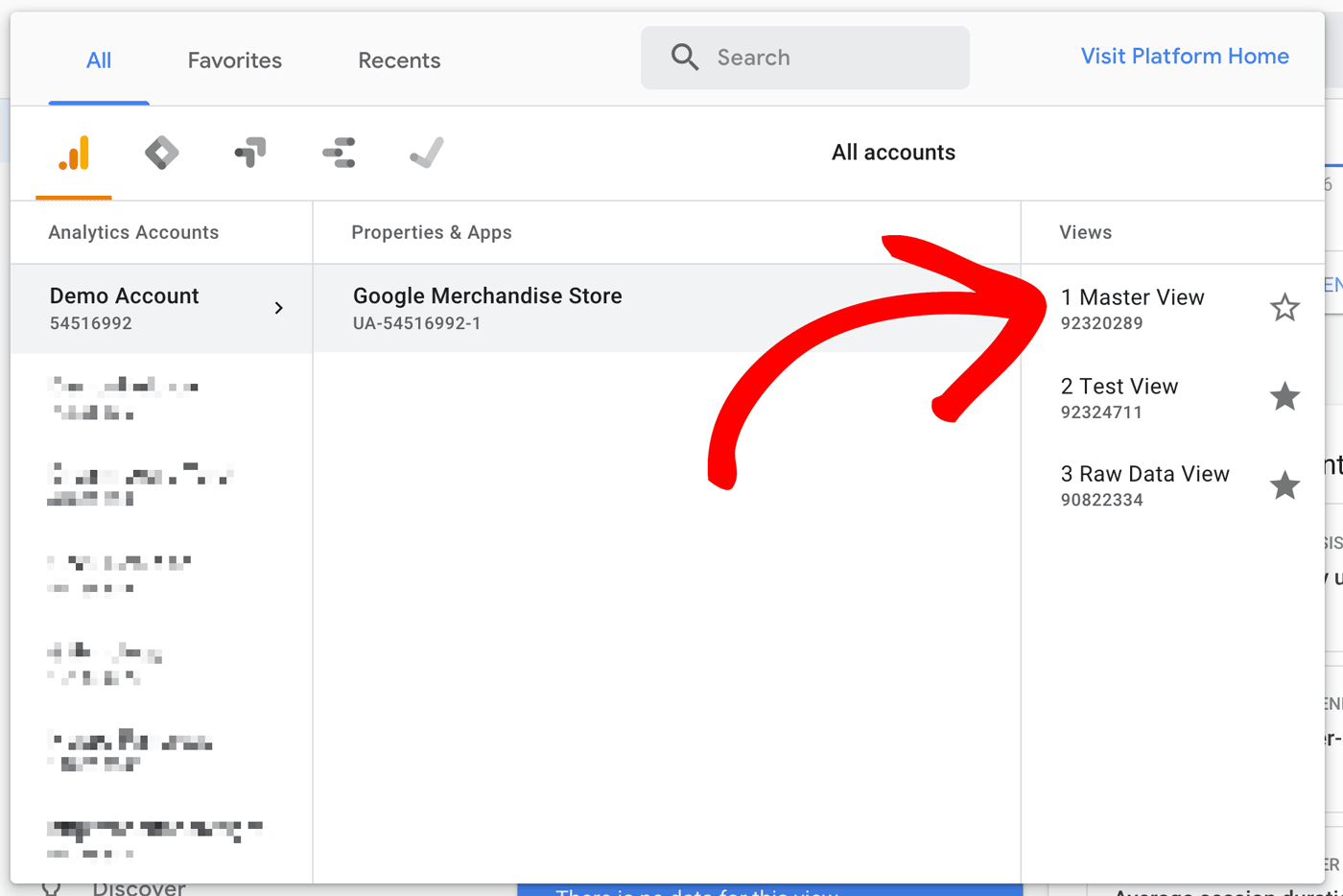
Step – 2. Now, click on Admin, gear icon, and the bottom left navigation.

Step – 3. Verify that the correct account and property are selected.

Step – 4. Click on GA 4 Setup Assistant which should be the first option in the Property column.

Step – 5. In the Setup Wizard, click on the large blue button that shows Get Started.

Step – 6. Finally, click on the blue button to create a property.

Note: You may need to add the Analytics tag by yourself if you use a website builder such as Shopify, WordPress, or Wix. The setup assistant of GA 4 works automatically with gtag.js.
Additionally, if you’re having problems with Google Analytics sync on your Settings page, ensure that you have old code on your site. If not, add your old UA code and resync your account.
Will There Be Any Loss Of Data If The Transition Isn’t Made On Time?
GA 4 does not carry any data that you’ve gathered on the old version. It uses an entirely new data model which requires a new implementation to insert data into that product.
So, the best practice immediately should be to run both versions, old and new, side by side so that the transition remains smooth, which is also the reason why businesses should switch to GA 4 by July 2022.
If this doesn’t happen on time, later on, it will harder for businesses to do a year-by-year analysis on Analytics. Hence, running GA4 in parallel with analytics is the best bet.
Currently, the focus should be on getting the key conversions tracked and not getting to-the-point data, especially, if you don’t have enough time to make the transition. With the right Google tag manager, it should be convenient to transition base pages.
How Is It Possible To Migrate Data From Universal Analytics To GA 4?
As of now, there doesn’t seem to be a major update on transitioning to Google Analytics 4. One shouldn’t be bothered with very old data and transferring relevant data would be convenient for all through Google sheets to get the usual tables or reports.
Just the basic data should be simple to transition. Though there might be plug-ins that are likely to become available for transitioning but relevant, yearly business data should be easy to transfer.
However, to move mass data, the best possible way would be through Google Sheet connectors as it allows for automation. In the coming months, some plug-ins for mass data transfer might also become available.
Moreover, Google Analytics 4 contains a lot of features in its free version such as funnels, Google Advanced Media Integration, Big Query Integration, Search Ads 360, etc.
This will aid marketers in collecting the raw data for their campaigns, so if, in the future, there’s any update in the version of Google Analytics, businesses won’t have trouble migrating data.
Benefits Of Google Analytics 4 Over Other Versions
The new modernized data model of GA 4 has taken tracking to a whole new level. These are some of the benefits of GA 4:
- Goals won’t be session scoped anymore. Type goals, seasonal goals, user scoped goals, and true counts, will all be possible with this version.
- Different dimension goals would also be possible to use. For instance, pages, and sessions can go together which can help us know the number of sessions per page.
- Many of the advanced features are available for free.
How The Bounce Rate Will Be Measured in GA 4?
Google Analytics has bought some changes to measuring bounce rate with the new update. Here are some things you should know:
- In the earlier versions, bounce-rates were devoid of any activity, and were single-page visits.
- Now, GA 4 will calculate events which it’s going to do automatically. For instance, 10 seconds of engagement on the page won’t be counted as a bounce.
- If a conversion was completed in less than 10 seconds of interaction, then it won’t be counted as a bounce.
- Thus, in GA 4, bounce rate is the percentage of sessions that were without engagement.
What Is Dual Tagging And Should You Do It?
Dual Tagging allows you to build GA 4 implementation, meanwhile, keeping Universal Analytics implementation. Thus, dual tagging is an approach that allows you to build a historical record in GA 4, while you continue to use Universal Analytics until you’re ready to switch over.
As more crucial features are getting added to GA 4 such as conversion rate, custom channel groupings, and more, most marketers are still analyzing data in Universal Analytics.
So, yes dual tagging is recommended as when you’ll switch over to GA 4, the complete GA 4 features will be implemented on the data collected.
Attribution Models In Google Analytics 4
Instead of the default model, users can now set their reporting attribution model. There are 3 attribution concepts in GA 4 you should know about:
- Attribution At A User Level: You can find this in the user acquisition report.
- Attribution At A Session Level: You can access this from the traffic acquisition report.
- Attribution At Conversion Level: You can observe this from the conversion report.
With these concepts, data can be presented in the way reporting attribution model was picked. Thus, it’s possible to get precise data as you can drill into individual engagements on a page and look at data from different reporting attribution models instead of the standardized approach.
How To Make The Best Out Of Google Analytics 4 Reporting?
Google Analytics is making a huge shift from a session-based model to an event-based model. Everything is about users and events. So, with these major updates, the Google Analytics tracking method has changed and so have the ways of reporting:
With GA 4, overview reports in summary cards are presented instead of a list of predefined reports for every use case.
The homepage of GA 4 shows the overall traffic, conversions, and revenue for that specific property. Thus, a homepage can give an overview of a property and can answer questions such as where are new users coming from, pages, and screens with the most views.
However, there are different types of reports that are capable of a specific task. These reports are:
1. Real-Time Report

From the left navigation, real-time reports can be accessed. It shows the events that happened within the last 30 minutes. These reports can be used to:
- Check if the tracking code is working or not.
- To measure the impact of an event in real-time.
It’s even possible to get data for a single user with the View User Snapshot available at the top right corner of the Real-Time report. It includes the user’s real-time activity with the site or app, device, location, etc.
2. Life Cycle Report

This includes the complete funnel of the customer cycle from acquiring a customer to selling and retaining them. It’s useful for closely analyzing user behavior, thus, answering two fundamental questions which are:
- How do users enter the funnel?
- How do they behave once they are in the funnel?
With reports on demographics and technology, as well as events and conversions, lifecycle reporting answers valuable insights.
3. User Lifetime Report

These reports aid marketers in building reports that can visualize which users are driving the highest lifetime revenue. Moreover, you can discover the marketing campaigns that are achieving the most valuable users. This includes customers with the highest purchase possibility.
4. Event Tracking
![]()
Once a property is established in GA 4, the setup automatically activates enhanced measurement in your GA 4 property. The most basic of tracking is automatic and ready to go, however, custom code might still be required for form submissions and to track third-party elements.
Explorer Reports: The New Analysis Feature
Explorer reports provide new, advanced techniques and a template gallery unlikely to be available elsewhere. Follow these steps to create a new analysis:
- Login into your Google Analytics account.
- Click on Analysis which is available in the bottom left navigation under Explore.
- Choose the technique you wish to analyze your data with.
Various Types Of Analysis
1. Funnel Analysis
To get in-depth data on how users complete an event, funnel analysis is probably the way to go. It can precisely explain how a user becomes a one-time user and then a repeat customer.
With a funnel analysis report, it’s easy to visualize the steps that shoppers take, and how they fail and succeed at each step.
2. Exploration
With exploration, a new set of configuration options are available that help explores new insights. Thus, it aids in representing your data in a manner that’s easy for anyone to understand.
Moreover, anomaly detection automatically highlights data that’s showing results outside of the expected limits.
3. Segment Overlap
Both Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4 properties use Segments. With GA 4, it’s now possible to build segments with multiple conditions so that you can arrange them into a condition group.
Those segments divide a specific group of users such as users from a specific city, users who perform a specific action, etc.
4. Path Analysis
With path analysis, a user can visualize the series of events that users triggered on their path of purchase. With this type of analysis, marketers can discover user behavior and study various patterns.
5. Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis groups users with a common characteristic This common characteristic could be anything from an event, conversion, or acquisition date.
Cohort Analysis reports could be utilized in situations like how long it takes for individuals to convert in response to a specific marketing tactic.
Conclusion
With a major change on the horizon, it’s better to be prepared before it’s too late. The deadlines are out so marketers should quickly adapt to GA 4.
With new exciting measures and updates, they should keep a tab on what’s changing and what’s new with GA 4. Only time will tell what the final GA 4 version will look like in terms of features, and UI.
